E invoicing performance optimization is the discipline of moving more validated e invoice documents through your stack in less time and with fewer errors. In Malaysia, the stakes are higher because performance ties directly to tax compliance, regulatory requirements, and the e invoicing regulations issued by the Inland Revenue Board within the national regulatory framework. E invoice implementation is now a mandatory regulatory requirement in Malaysia, requiring organizations to transition to electronic invoicing, fulfill compliance obligations, and adopt suitable systems to meet IRBM standards. When you optimize early, you improve operational efficiency, reduce costs across billing and collections, protect sensitive financial data, and implement e invoicing in a way that scales with growth rather than buckling under it.
Performance is not just an IT goal. It is a compliance goal. Faster submissions lower the chance of end-of-month pileups, safer data flows reduce non compliance risk, and well-designed workflows strengthen evidence during tax audits. Whether you operate business to business, business to consumer, or business to government, a high-throughput e invoicing system pays dividends in cash-flow timing, finance productivity, and management visibility. However, such a transition from paper-based to electronic invoicing systems requires careful planning, support, and training to address challenges and ensure a smooth changeover.
Introduction to E-Invoicing
E-invoicing, or electronic invoicing, is transforming the way Malaysian businesses handle their invoicing processes. Instead of relying on paper invoices, e invoicing enables the digital generation, transmission, and receipt of invoices, making the entire process faster, more secure, and more transparent. The Inland Revenue Board (IRB) of Malaysia has introduced e invoicing regulations as part of a broader initiative to improve tax compliance, streamline tax administration, and enhance business operations across the country.
By mandating e invoicing for all Malaysian taxpayers undertaking commercial activities by 2025, the IRB aims to reduce tax evasion, increase operational efficiency, and support the growth of Malaysia’s digital economy. E invoicing not only helps businesses meet regulatory requirements but also reduces costs associated with manual handling, paper storage, and error correction. As Malaysia moves toward a fully digital tax administration system, e invoicing is set to become a cornerstone of efficient, compliant, and future-ready business operations.
E Invoicing Performance Optimization
Successful e invoicing performance optimization starts with three levers: throughput, accuracy, and resiliency. Throughput means your architecture can handle daily volumes and end-of-period spikes without timeouts. Accuracy ensures every document meets e invoicing requirements on the first pass. Resiliency protects you from transient failures network blips, rate limits, and integration hiccups without generating duplicates or partial records.
A practical approach combines process discipline with technology choices. On the process side, standardize your invoicing processes across entity types and ensure approvals are clear. On the technology side, prefer event-driven queues over sequential processing, adopt idempotency keys to prevent double posting, and implement structured retries with exponential back-off. Embracing technological advancements is crucial to overcome resistance to change and facilitate e invoicing performance optimization. When these fundamentals are in place, the Inland Revenue Board workflows feel routine: you prepare, issue e invoice, receive a validated e invoice response, and move on with clean financial records.
Success indicators
- Faster end-to-end cycle time from draft to validated e invoice
- Lower error rates across e invoice data and master data
- Stable throughput during month end, tax return preparation, and audits
- Clear audit trails that support tax audits, reduce non compliance risk, and improve tax compliance
If you manage by numbers, monitor cycle time from draft to validated e invoice, and track your first-pass yield (accepted on first submission). Watch P95 and P99 latency at cutover, and measure the proportion of manual tasks per thousand invoices. Over time, e invoicing performance optimization should produce lower error rates across e invoice data, stable throughput around month end and tax return activities, and audit trails that clearly demonstrate tax compliance.
Business Operations Best Practices
Performance begins with business operations. Treat e invoicing as a cross-functional program that aligns finance, IT, and compliance around shared objectives. Start by mapping business processes across business to business, business to consumer, and business to government flows. Each flow has different timing, document combinations, and exception scenarios, credit notes, debit notes, and non business transactions all need rules you can enforce repeatedly.
Align your invoicing processes with e invoicing regulations and e invoicing guidelines published by the authorities. Document who approves, who posts, and who reconciles. Then automate the hand-offs so approvals become electronic document events that trigger the next step without email back-and-forth. Version-controlled storage with role-based access ensures that only the right users can change sensitive fields and that every change is tracked.
From a tax administration perspective, clarity matters. A buyer’s information, seller’s information, SST/GST fields where applicable, and line-item tax codes must be consistent across your relevant systems. This consistency is what keeps tax audits simple and keeps your organization on the right side of regulatory compliance.
E Invoicing In Malaysia Improves Efficiency
In Malaysia, e invoicing replaces paper invoices with electronic invoicing that is validated almost in real time. The move away from paper invoices is more than digitization. It is a structural shift toward real time data that makes cash-flow forecasting easier and dispute handling faster. Malaysian businesses usually choose between a direct Application Programming Interface integration and managed e invoicing solutions. The right path depends on system readiness, the complexity of existing systems, and your appetite for upfront investment.
From an operations lens, e invoicing in malaysia is about speed and control. With automated checks and consistent status feedback from the e invoicing system, your team can resolve rejections early, avoid end-of-month logjams, and cut repeat work. From a compliance lens, validated e invoice responses provide a provable, time-stamped history that helps improve tax compliance and discourages tax evasion through better traceability.
Why this change pays off
Transitioning to electronic invoicing reduces costs by trimming exception handling and manual rekeying. It shortens the path from delivery to invoice to payment, which improves working capital. And because your ledgers are backed by structured, consistent e invoice data, period-end reviews become “check the dashboard” instead of “search the archive.”
E-Invoice Management
Effective e-invoice management is essential for businesses seeking to maximize the benefits of e invoicing while ensuring compliance with Malaysia’s regulatory framework. E-invoice management covers the entire lifecycle of an invoice—from creation and validation to secure storage and easy retrieval. To stay compliant with e invoicing regulations, businesses must implement robust processes that guarantee data accuracy, maintain clear audit trails, and protect sensitive financial data at every stage.
Best practices in e-invoice management include integrating e invoicing systems with existing business processes, automating validation checks, and ensuring that all credit notes, debit notes, and non business transactions are handled according to regulatory requirements. Centralized management of e invoices across business units enables consolidated reporting, simplifies tax audits, and supports timely tax return preparation. By adopting a disciplined approach to e-invoice management, Malaysian companies can ensure compliance, improve operational efficiency, and build a strong foundation for digital transformation.
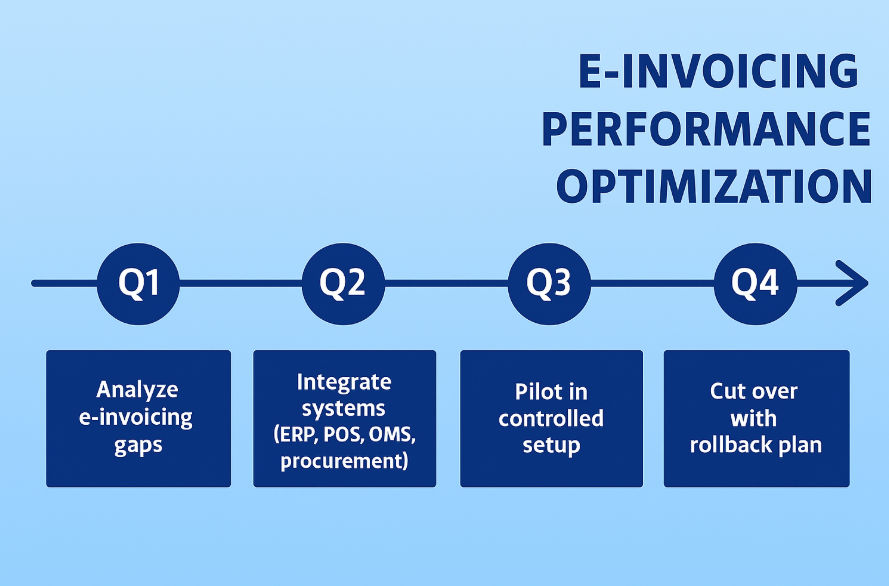
E Invoicing Implementation Timeline
Your internal plan should mirror the e invoicing implementation timeline set by the authorities. Take inventory of all Malaysian taxpayers in your group—malaysian companies, business trusts, and property trust funds—and map their go-live windows. The purpose is to avoid last-minute rushes that strain people and systems.
A simple cadence works well:
- Quarter 1: Perform a gap analysis on e invoicing requirements. Clean master data, agree on document variants, and finalize an implementation timeline that includes buffer time.
- Quarter 2: Integrate relevant systems. Connect ERP, POS, OMS, and procurement, normalize tax codes and units and start volume testing.
- Quarter 3: Pilot in a controlled environment. Run a parallel period and produce a consolidated e report that finance can compare to legacy statements.
- Quarter 4: Execute cutover with documented rollback steps. Stabilize, monitor KPIs, and refine dashboards for leadership.
Capacity planning should consider your annual turnover and annual revenue forecasts. If your growth is steep, provision message throughput and compute for the peaks, not the average.
E Invoicing Implementation Checklist
Implementation fails when people treat it as “just another IT integration.” Treat it as business transformation with careful planning across discovery, integration, testing, and go-live.
Discovery and design
Clarify your e invoicing models and how they map to chart-of-account elements, tax codes, pricing units, and payment terms. Decide how you will handle adjustments (credit notes, debit notes), non business transactions, and unusual scenarios. Document regulatory compliance checkpoints and the approvals required before an invoice can be posted.
Integration and data
Connect each upstream application to your e invoicing system through secure APIs. Validate buyer and seller master data to ensure you can issue e invoice without friction. Make sure addresses, state codes, emails, and phone numbers follow format rules, small errors here cause big slowdowns later. Where possible, enrich data at ingress so your downstream payloads are complete and consistent.
Testing and pilot
Run stress tests with realistic volumes to reveal throughput limits. Observe error codes and tune concurrency. Reconcile consolidated e invoice summaries with the general ledger to prove that documents, journals, and reports all match. Make rejections visible, not hidden, the faster you see them, the faster you fix them.
Go live and scale
At go live, monitor P95/P99 latency, retry ratios, and first-pass acceptance. Adjust worker counts to avoid rate-limit pushback. Keep resource allocation flexible enough to handle month-end and quarter-end surges without overtime firefighting.
Common Challenges in E-Invoicing
While the benefits of e invoicing are clear, Malaysian businesses often encounter several challenges during implementation and ongoing operations. Integrating e invoicing solutions with legacy systems can be complex, especially when dealing with multiple platforms and data formats. Ensuring data accuracy is another common hurdle, as even minor discrepancies in master data or tax codes can lead to rejections and delays.
Change management is critical, as teams must adapt to new workflows and regulatory requirements. Handling exceptions such as credit notes, debit notes, and non business transactions requires clear rules and automated processes to avoid manual errors. Data security is also a top concern, with businesses needing to safeguard sensitive financial data against breaches and unauthorized access. Finally, resource allocation and system readiness can be strained during peak periods, increasing the risk of non compliance and operational bottlenecks. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, investment in the right technology, and ongoing training to ensure e invoicing compliance and sustained performance improvement.
Data Security Controls For E Invoicing Systems
Security is non-negotiable. You’re handling sensitive financial data and must guard against data breaches without sacrificing performance.
Use TLS for every API call and rotate certificates on a schedule. Sign payloads where appropriate to protect electronic document integrity. Implement role-based access in both the ERP and the e invoicing system so that no single person controls creation, approval, and posting. Encrypt tokens, keys, and e invoice data at rest, and use least-privilege access patterns in your vault. Finally, watch your logs: flagged, failed, and unusual attempts should trigger alerts so you can respond before risk escalates.
Good security improves trust during tax audits. When auditors see clear segregation of duties and consistent controls, they can focus on the substance of transactions rather than wrestling with basic access issues.
Data Accuracy Techniques
Data accuracy is the foundation of throughput. The fastest system in the world still fails if the data is wrong. Enforce field lengths and formats, and validate tax IDs for taxpayers undertaking commercial activities before submission. If you maintain multiple customer masters for different business lines, harmonize them now to avoid conflicting records.
Align pricing units, tax codes, and rounding rules across relevant systems so line totals and document totals always balance. Keep annual revenue and annual turnover consistent with finance reporting, reconcile them against consolidated e invoice summaries during period close. Clean masters not only prevent rejections, they also prevent small mismatches from accumulating into larger reconciliation problems.
When you do encounter implementation challenges, solve them once in the central schema rather than patching per system. This is how you reduce manual tasks and keep e invoicing performance optimization on track.
Digital Economy Readiness for Malaysian Companies
Malaysia’s digital economy strategy benefits when organizations submit accurate, timely, and traceable documents. That traceability allows authorities to streamline tax administration while giving businesses reliable real time data for operational decisions. Transparent flows discourage tax evasion because there’s less room for mismatches to hide, and they help the Inland Revenue Board focus on targeted reviews rather than broad fishing expeditions.
For management teams, better data translates into metrical insight: DSO trends, dispute rates, average acceptance latency, and exception rates by business unit. When these metrics are visible, leaders make faster decisions about staffing, credit terms, and cash-flow scenarios.
Application Programming Interface Integration
An Application Programming Interface-first approach provides the control you need to hit throughput targets. Design your API layer with idempotency keys so repeated submissions cannot create duplicate validated e records. Batch intelligently to avoid timeouts, watch rate-limit headers and adjust concurrency rather than forcing retries that clog queues.
Capture validation responses as first-class events. When a document becomes a validated e invoice, attach QR details, update the customer record, trigger buyer notifications, and reflect the status in AR. Instrument everything: collect throughput, error codes by reason, and latency at P50/P95/P99 so tuning decisions are based on data, not hunches. Over time, your telemetry becomes evidence of control and maturity. It is a signal that your organization takes regulatory compliance seriously.
Cost Reduction Playbook For E Invoicing Optimization
There is an upfront investment in integration and change management, but the cost reduction is real and recurring. As e invoicing performance optimization improves, your team spends less time on exception queues and manual rework. That translates into fewer nights and weekends at month end, lower overtime, and fewer escalations from sales or customer service.
Clean, validated data reduces penalties related to non compliance and makes tax return preparation straightforward. Predictable processing also reduces the need for oversized infrastructure because you’re no longer compensating for chaos with brute force. Instead, you scale deliberately, add workers when needed, and pause them when demand falls.
Annual Turnover Planning For E Invoicing
Capacity should be sized for your expected growth, not just today’s volumes. Annual turnover and annual revenue forecasts help you plan message throughput, licensing, and infrastructure with enough headroom for peak days and audit windows. If acquisitions or new product lines are on the horizon, model their impact now. It’s far cheaper to book capacity early than to scramble during cutover.
Two practical tips:
- First, load-test with the peaks you actually experience (month end, quarter end, campaign dates), not a flat average.
- Second, stress test your exception flows. Many systems perform well on perfect data and then crumble when exceptions surge, credit notes, debit notes, and non business transactions all deserve a real workout before you go live.
Digital Tools Stack For E Invoicing
Your digital tools should create resilience and transparency, not complexity. Use durable queues and worker pools for parallel processing, let the queue absorb spikes and keep upstream systems snappy. Add validation services that check tax IDs and schema rules before submission. Build dashboards that expose success rates, retries, and P99 latency by endpoint and by business unit so leaders see the reality in one place.
Finally, protect the keys to the kingdom like keep credentials, certificates, and tokens in a secure vault with rotation policies and audit logs. These basic controls are part of regulatory requirements in many industries and make life easier when auditors ask for evidence.
Case Studies Across B2B B2C B2G
Business to business distributor
A distributor integrated ERP and warehouse systems through an API-based e invoicing system. By validating master data early and splitting batches, they increased first-pass yield, received faster validated e responses, and stayed within regulatory compliance while improving cash-flow visibility.
Business to consumer retailer
A retailer replaced paper invoices with electronic document flows at POS. Exceptions fell, customer copies arrived instantly, and service tickets dropped. The result was measurable operational efficiency and fewer risks of non compliance.
Business to government services
A services provider aligned contract terms to e invoicing requirements, automating credit notes and debit notes. Dispute cycles shortened, and month-end consolidated e reporting became straightforward, helping to ensure compliance during tax audits. Real-time data capture from e invoicing enables tax authorities to conduct more efficient, risk-based tax audit processes using advanced analytics and targeted reviews.
E-Invoicing and Supply Chain Management
E-invoicing is a game-changer for supply chain management in Malaysia, offering greater efficiency, transparency, and control across business to business and business to government transactions. By digitizing invoicing processes, companies can exchange validated e invoices in real time, reducing delays and minimizing disputes with suppliers and customers. This real time data flow enhances traceability, making it easier to track goods, payments, and tax obligations throughout the supply chain.
With e invoicing, businesses benefit from streamlined tax administration, as every transaction is automatically recorded and compliant with Inland Revenue Board requirements. This not only improves tax compliance but also fosters better collaboration between supply chain partners. Automated workflows reduce manual intervention, cut down on errors, and ensure that all parties have access to accurate, up-to-date information. As a result, Malaysian businesses can respond more quickly to market changes, optimize inventory management, and build stronger, more resilient supply chains.
E-Invoicing and Financial Management
The adoption of e invoicing has a significant impact on financial management for Malaysian companies. By automating the creation, validation, and storage of e invoices, businesses can maintain accurate financial records, simplify tax return preparation, and ensure compliance with the Income Tax Act and other regulatory requirements. E invoicing solutions provide real time visibility into cash flow, enabling finance teams to make informed decisions and implement effective performance improvement plans.
With consolidated e invoice data, organizations can easily reconcile accounts, monitor payment cycles, and identify trends that support strategic financial planning. The reduction in manual tasks and paper-based processes leads to cost savings and minimizes the risk of errors or non compliance. Ultimately, e invoicing empowers Malaysian businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain a strong financial position in an increasingly digital economy.
Governance And Reporting That Improves E Invoicing Compliance
Governance keeps improvements durable. Produce monthly consolidated e summaries for leadership so trends are visible and resourcing decisions are evidence-based. Run internal reviews that look for patterns that could trigger non compliance, recurring rejections, specific units with higher exception rates, or repeated late postings. Keep an end-to-end audit trail for each electronic document event so interactions with the Inland Revenue Board are short, courteous, and well-documented.
Conclusion
Caltrix designs and delivers scalable e invoicing solutions that meet regulatory requirements while maximizing performance. We integrate relevant systems, secure financial data, and align workflows so Malaysian companies can adopt e invoicing, streamline tax administration, and realize sustainable efficiency gains. We also connect seamlessly to cloud accounting platforms like Xero via API, ensuring validated e invoice data posts to ledgers with clean reconciliations, tidy audit trails, and zero copy-paste.
Ready to optimize e invoicing and Xero together for greater efficiency? Talk to Caltrix today for a tailored implementation plan that fits your e invoicing implementation timeline, integrates with your existing systems, and unlocks cost reduction without compromising data security or data accuracy.